The merge() and join() methods are the DataFrame method, not a series method. The concat() method is the pandas’ method which provides the functionality to combine the pandas’ objects such as DataFrame and Series.
Merge –
- The merge() function used to merge the DataFrames with database-style join such as inner join, outer join, left join, right join.
- Combining exactly two DataFrames.
- The join is done on columns or indexes.
- If joining columns on columns, the DataFrame indexes will be ignored.
- If joining indexes on indexes or indexes on a column, the index will be passed on.
Join –
- The join() function used to join two or more pandas DataFrames/Series horizontally.
- Join() uses
mergeinternally for the index-on-index (by default) and column(s)-on-index join. - Aligns the calling DataFrame’s column(s) or index with the other objects’ index (and not the columns).
- Defaults to left join with options for right, inner and outer join
Concat –
- concatenate two or more pandas DataFrames/Series vertically or horizontally.
- Aligns only on the index by specifying the axis parameter.
- Defaults to outer join with the option for inner join
Syntax
DataFrame.merge(self, right, how='inner', on=None, left_on=None, right_on=None, left_index=False, right_index=False, sort=False, suffixes=('_x', '_y'), copy=True, indicator=False, validate=None)
DataFrame.join(self, other, on=None, how='left', lsuffix='', rsuffix='', sort=False)
pandas.concat(objs, axis=0, join='outer', join_axes=None, ignore_index=False, keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False, sort=None, copy=True)
Examples
In [1]:
# Let's Define the DataFrames
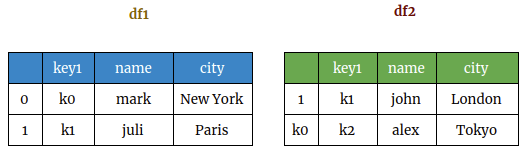
import pandas as pd
data1 = {'key1':['k0','k1'], 'name' :['mark','juli'],'city':['New York','Paris']}
data2 = {'key1':['k1','k2'],'name' :['john','alex'],'city':['London','Tokyo']}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1,index = [0,1],columns=['key1','city','name'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2,index=[1,'k0'],columns=['key1','city','name'])
Merge() –
In [2]: df1.merge(df2,on="key1") Out[2]: key1 city_x name_x city_y name_y 0 k1 Paris juli London john
Join() –
In [3]: df1.join(df2, lsuffix='_') Out[3]: key1_ city_ name_ key1 city name 0 k0 New York mark NaN NaN NaN 1 k1 Paris juli k1 London john In [4]: df1.join(df2, on="key1",lsuffix='_') Out[4]: key1_ city_ name_ key1 city name 0 k0 New York mark k2 Tokyo alex 1 k1 Paris juli NaN NaN NaN
Concat() –
In [5]: pd.concat([df1,df2]) Out[5]: key1 city name 0 k0 New York mark 1 k1 Paris juli 1 k1 London john k0 k2 Tokyo alex In [6]: pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1) Out[6]: key1 city name key1 city name 0 k0 New York mark NaN NaN NaN 1 k1 Paris juli k1 London john k0 NaN NaN NaN k2 Tokyo alex
. . .