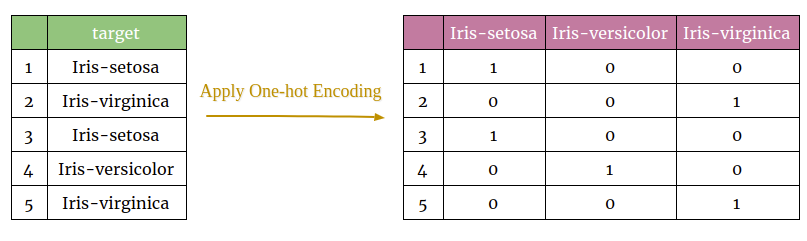
Pandas’ get_dummies() method used to apply one-hot encoding to categorical data.
Syntax:
pandas.get_dummies(data, prefix=None, prefix_sep='_', dummy_na=False, columns=None, sparse=False, drop_first=False, dtype=None)
Parameters
data - Series/DataFrame
prefix - (default None)String to append DataFrame column names.
prefix_sep - (str, default ‘_’). prefix separator to use.
dummy_na - (default False)Add a column to indicate NaNs, if False NaNs are ignored.
columns - (default None)Column names in the DataFrame to be encoded.
If None, all categorical features are encoded.
sparse - (default False)encoded columns return in SparseArray(True) or
in Numpy Array(False).
drop_first - (default False)Whether to get k-1 dummies out of k categorical levels
by removing the first level.
dtype - (default np.uint8)Data type for new columns. Only a single dtype is allowed.
Example – 1
Let’s see the example to understand how one-hot encoding work with categorical columns.
In [1]:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'student_name' : ['Tom','Mark','John','Neck'],
'Grade' : ['A','C','B','A']})
df
Out[1]:
student_name Grade
0 Tom A
1 Mark C
2 John B
3 Neck A
In [2]: new_df = pd.get_dummies(df,columns=['Grade']) In [3]: new_df Out[3]: student_name Grade_A Grade_B Grade_C 0 Tom 1 0 0 1 Mark 0 0 1 2 John 0 1 0 3 Neck 1 0 0
Example – 2
Let’s see how the pd.get_dummies() method work with NaN value.
In [4]:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame({'student_name' : ['Tom','Mark','John','Neck'],
'Grade' : ['A','C','B',np.nan]})
df
Out[4]:
student_name Grade
0 Tom A
1 Mark C
2 John B
3 Neck NaN # Neck' Grade is NaN
In [5]: new_df = pd.get_dummies(df,columns=['Grade']) new_df Out[5]: student_name Grade_A Grade_B Grade_C 0 Tom 1 0 0 1 Mark 0 0 1 2 John 0 1 0 3 Neck 0 0 0
pd.get_dummies() method ignore the NaN value while encoding. If you want to consider the NaN value, use parameter dummy_na = True.
In [6]: new_df = pd.get_dummies(df,columns=['Grade'],dummy_na=True) # use dummy_na = True new_df Out[6]: student_name Grade_A Grade_B Grade_C Grade_nan 0 Tom 1 0 0 0 1 Mark 0 0 1 0 2 John 0 1 0 0 3 Neck 0 0 0 1
. . .