Training very deep neural network on a large dataset takes a lot amount of time sometimes it takes a day, weeks. Instead of training model each time, we should save the trained model and make a prediction for test data using that saved model.
Keras API provides the function for saving and loading trained models. This tutorial has explained to save a Keras model to file and load them up to make a prediction.
Generally, we required to save the trained model’s weights, model architecture, model compilation details and optimizer state to make a prediction on a new observation using a saved model.
Save a Keras Model
We can save the Keras model by just calling the save() function and defining the file name. It will generate the .H5 file. Let’s see the example to train a CNN on MNIST data.
In [1]:
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Dense, Flatten, Dropout
from keras.optimizers import SGD
(trainX, trainy), (testX, testy) = mnist.load_data()
trainX = trainX.reshape((trainX.shape[0], 28, 28, 1))
testX = testX.reshape((testX.shape[0], 28, 28, 1))
trainY = to_categorical(trainy)
testY = to_categorical(testy)
train_norm = trainX.astype('float32')
test_norm = testX.astype('float32')
train_norm = train_norm / 255.0
test_norm = test_norm / 255.0
num_classes = 10
def prepare_model():
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(32,kernel_size=(3,3),activation='relu',input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy",optimizer="adam",metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
model = prepare_model()
model.fit(train_norm, trainY, batch_size=128,validation_split=0.2,epochs=1,verbose=1)
model.save("trained_model.h5")
This will train the model and save the model in the current directory.
Load a Keras Model
Keras provides load_model() function to load the saved model by specifying the file name. This method returns the model with its architecture and weights.
Let’s load the above saved model and evaluate new test data.
In [2]:
from keras.models import load_model
model = load_model('trained_model.h5')
model.summary()
Out[2]:
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 26, 26, 32) 320
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 24, 24, 64) 18496
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling2 (None, 12, 12, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 12, 12, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 9216) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 128) 1179776
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290
=================================================================
Total params: 1,199,882
Trainable params: 1,199,882
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
In [3]:
score = model.evaluate(test_norm, testY, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
Out[3]:
Test loss: 0.059910419065877796
Test accuracy: 0.9808
. . .
Make Prediction
As we all know our model is trained on 28*28 grayscale images. So, to make a prediction of a new image, the image must be grayscale and the size of it is 28*28.
Let’s make a prediction on a below image. You can download this image in your current directory and save it with the file name test_fig.jpg.
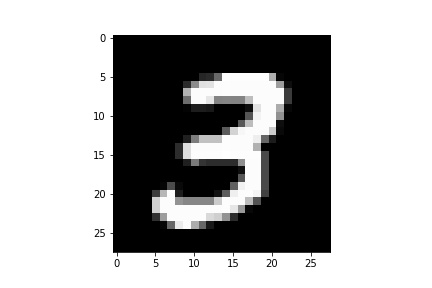
Here, we need to pre-process the test input image same as train image.
In [4]:
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from keras.models import load_model
def load_image(filename):
# load the image
img = load_img(filename, grayscale=True, target_size=(28, 28))
# convert to array
img = img_to_array(img)
# reshape into a single sample with 1 channel
img = img.reshape(1, 28, 28, 1)
# prepare pixel data
img = img.astype('float32')
img = img / 255.0
return img
In [5]:
img = load_image('test_fig.jpg')
model = load_model('trained_model.h5')
digit = model.predict_classes(img)
print("Predicted digit : ",digit[0])
Out[5]:
Predicted digit : 3